The dynamic world of sustainable manufacturing is where modern business meets environmental responsibility. Understanding the future of manufacturing requires knowledge of the critical goals, business challenges, and technologies needed to digitize the industry. From IoT (Internet-of-Things), ESG software, paperless factories and AR training, sustainable production will change the industry sooner or later. In this article, I explain how these changes are advantageous to the environment, offer economic profits, and increase supply chain resilience.
What is sustainable manufacturing? What is a sustainable factory?
A sustainable factory means creating goods in an ecologically friendly and resource-efficient manner. Some business leaders may view sustainability as costly and predict potential roadblocks; however, incorporating sustainability into the industry has, in fact, many current benefits. The 2023 Energy Efficiency Impact Report highlights that since 1980, investments in energy efficiency have reduced nearly $800 billion in annual energy expenditures in the U.S. and decreased energy consumption per household by 16%.
And how about sustainable factories? They are key in Industry 4.0, adopting technologies like big data analytics and IoT technology to optimize operations. These digital tools improve quality control, waste management, and help making informed decisions. With predictive maintenance, costs and downtime are reduced. Leaders like Amazon are advancing towards fully automated operations, a crucial step in enhancing manufacturing efficiency and meeting customer needs in Industry 4.0.
The most important goals of ESG manufacturing
The most crucial goals of ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) manufacturing are fundamentally about balancing profitability and sustainability:
- environmental impact reduction: lowering emissions, minimizing waste, and efficiently using resources.
- social responsibility: ensuring fair labor practices and creating a safe, inclusive workplace.
- governance and ethics: upholding transparency, ethical business practices, and regulatory compliance.
These goals integrate ESG principles into manufacturing, addressing environmental concerns while enhancing long-term business viability and public trust. Adopting these objectives contributes to a healthier planet and ensures sustainable business success.
The biggest challenges of sustainable manufacturing
The biggest challenges of sustainable manufacturing lie in balancing environmental responsibility with practical business needs. Some of the most crucial challenges include:
- Cost Implications
Sustainable practices often require a substantial initial investment, including new technology adoption and industrial training, posing a financial challenge for many companies.
- Technological Integration
Transitioning to sustainable methods requires advanced technology, with integrating into existing systems being particularly challenging for older facilities.
- Regulatory Compliance
Maintaining complex environmental regulations demands continuous attention and adaptability, making compliance daunting.
- Supply Chain Sustainability
Achieving sustainability across the supply chain is complex, involving a company’s operations and its suppliers’ practices.
- Consumer Expectations
Meeting consumer demands for eco-friendly products while maintaining cost-effective production presents a significant challenge.
To navigate these challenges, companies must cleverly balance short-term business objectives with a vision for long-term sustainability, a key ingredient for the future of sustainable manufacturing.
Social Responsibility in Sustainable Manufacturing
In sustainable production, a socially responsible approach requires more than just adopting environmentally friendly technologies. It’s about creating a work environment that values and supports employees.
Leaders must ensure fair labor practices, uphold ethical standards, provide fair compensation, and maintain transparent policies. Security is key and can be improved with factory automation, paperless softwares, sustainable factories, and IoT, providing safer environments.
Sustainable Manufacturing: Technologies
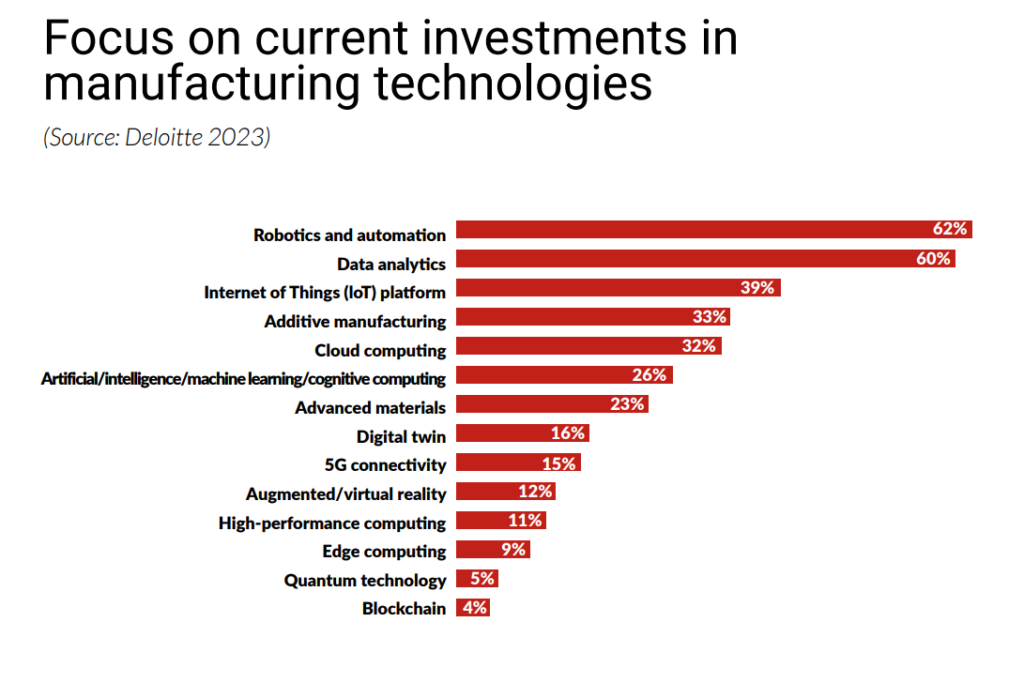
Sustainable manufacturing technologies are revolutionizing companies’ operations and contributing to environmental conservation. Key technologies include:
Industrial Automation
Automation in manufacturing significantly enhances industry sustainability by improving efficiency and reducing waste. Key elements include automated quality control for early defect detection, reducing material waste, and using robots and AI in waste management to increase recycling efficiency. Additionally, automated vehicles and robots optimize material handling, conserving energy. These advancements highlight the essential role of automation in promoting eco-friendly and efficient manufacturing.
Paperless Manufacturing
Sustainable manufacturing, crucial for the environment, often misunderstands the role of paperless manufacturing. It’s more than just cutting paper; it’s about integrating paperless softwares and digitization to boost efficiency and reduce waste. This approach helps manufacturers minimize resource use and aligns with broader ESG goals. Companies use digitalization in the industrial machinery and equipment sector to achieve greater efficiency and transparency, fostering a sustainable and resilient manufacturing system.
Industrial Digitization
IoT and artificial intelligence are currently driving the digitization of the industry. IoT devices can provide precise monitoring and control through their ability to collect data in real-time. This, in turn, is a simple way to optimize production and efficiency. Artificial intelligence streamlines the process by analyzing data for predictive maintenance and improving supply chains.
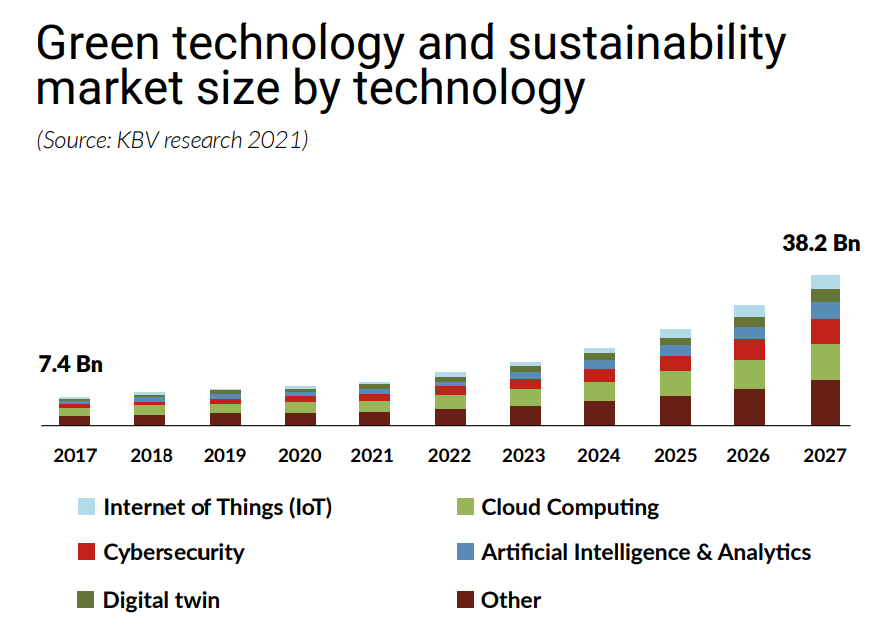
Condition Monitoring & Predictive Maintenance
Other forms of ESG implementation in the industry, including machinery repair and maintenance, are condition monitoring and predictive maintenance. These strategies ensure equipment efficiency, which is crucial for machinery repair and maintenance. They lead to less waste, energy conservation, and an extended lifespan of machinery. This approach is key in reducing carbon emissions and aligning with environmental regulations. Ultimately, it contributes to cost savings by minimizing downtime and optimizing machinery repair and maintenance resource usage.
ESG Software
ESG software will play a key role in sustainable production in the 21st century. How? Giving people the tools to manage and report on sustainability metrics. ESG software helps, for example, track environmental impacts, social responsibilities, and management practices. Monitor carbon footprints, energy consumption, waste management, work practices, and regulatory compliance.
AR Manufacturing Training
Augmented reality (AR) is revolutionizing manufacturing training, epitomizing the ethos of Industry 4.0. It empowers industrial integrators by offering interactive virtual simulations that enhance skill development while minimizing the need for physical resources. This shift towards AR in training supports paperless manufacturing, replacing outdated training manuals with dynamic digital content, thereby contributing to eco-friendly practices. AR is an indispensable tool in contemporary, sustainable manufacturing processes by keeping training aligned with the latest industry standards.
When it comes to AR technology, it is worth including digital workflows in the training of production workers. It is easy-to-use software that allows you to create interactive, multimedia-rich content. An example is Nsflow, designed to reduce errors and operational costs while providing consistent, high-quality training, and reducing reliance on individual expertise.
Conclusion

Innovative technologies in sustainable production, including electronic systems, paperless softwares, and digitalization, offer more than just environmental benefits; they increase operational efficiency and profitability. Companies are implementing paperless production, automation, or AR training, aiming for broader ESG goals. This approach includes using digital tools to ensure more efficient and transparent processes, contributing to environmental sustainability and operational resilience.


























