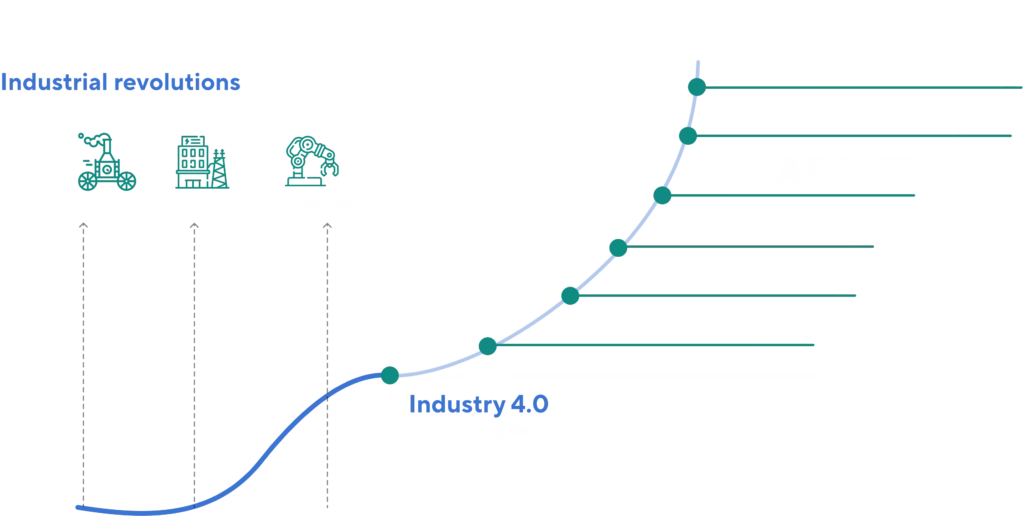
It’s revolutions that shift industrial dynamics. Humanity passed the road from agricultural societies to the world as we know it today in a few leaps, named Industrial Revolutions. As old methods become insufficient, productivity advancement requires taking the next big step forward.
Transitions to new manufacturing processes
1st Industrial Revolution
The change from manual labor to using machines running on steam
2nd Industrial Revolution
Machines became more powerful and efficient with electricity, humanity gained better communication thanks to the invention of the telegraph and the telephone
3rd Industrial Revolution
Use of nuclear energy, the growing potential of electronics, space conquest
4th Industrial Revolution
The merge of manufacturing and industrial technologies with modern digital solutions.
Now that we know what the revolution is, what is it exactly?
The 4th Industrial Revolution drives the search for new opportunities to improve innovations, efficiency, and quality of produced goods. The below solutions were known to humanity – or at least, the more tech-savvy part of it – but their significance changed recently, and are not believed to be marginalized any time soon.
Cloud computing
The cloud is widely known as the convenient solution for online data storage, utilizing remote servers instead of users’ own drives. The term cloud is broad and covers an array of managed services, which may include infrastructure, data, network, and security management. Cloud providers cost-efficient solutions enabling scaling projects, easy implementation to online-stored assets, and safe collaboration on remotely accessed products, immune to threats affecting applications stored on on-site servers.
Internet of Things
It’s not just our phones that became smart over recent years. The more applications are created, the more devices become smart. Or is it the other way around? Anyhow, we’re witnessing the dynamic growth of a network of physical objects provided with software, sensors, and other technologies enabling connectivity and data exchange. IoT connects the devices to the cloud for enhanced data collection, streamlining processes.
Connected appliances serve various purposes, from on-site beacons recognizing entering employees, agricultural sensors verifying the state of the crops, detectors supporting oversight of production lines, and supply chains.
Edge computing
Contrary to cloud computing, the edge is developed to serve a role in on-site or neighborhood computing, minimizing the need for remote data centers. The future has already prepared some roles for the edge, as it can be used in e.g. driving autonomous vehicle convoys, and in the industrial world, preferably in predictive maintenance. This model of computing allows for rapid data collection and processing, letting the beacons and sensors monitor machinery, predicting with low latency upcoming events requiring staff’s attention.
Augmented and virtual reality
Augmented reality allows performing actions in the real world, enhanced with digital additions, while virtual reality offers fully immersive experiences. The more complex the end-product, the greater the field day for AR-powered solutions. Assembly executed under the watchful eye of augmented reality is gaining popularity in various manufacturing facilities. AR is appreciated especially in the automotive industry, as a complete car build needs on average an astonishing number of 30.000 pieces!

presentation to try
Nsflow in action
Big Data
Large data sets cover data gathered at every stage of industrial processes. Their potential is appreciated in understanding customers more efficiently, reducing production costs, and eliminating excessive waste. Manufacturing companies utilize sensors to collect data used later in the process to support automation and mechanization, as well as in – broadly speaking – cost reduction, achieved for example through investigating new materials and strategies.
Artificial intelligence
AI finds application in various industry fields, improving the way processes are carried out. One of its great uses is forecasting the behavior of machinery and supporting operators with predictive maintenance, reducing costs of downtimes. AI algorithms help streamline data analysis, manufacturing optimization, supervision of the manufacturing process from design, assembly of basic components to delivering the working solution.
How does modern manufacturing benefit from Industry 4.0?

It’s not just the technology changing industries on its own. It’s how modern solutions are applied. The list of improvements is constantly extending, as inventors, rationalizers, and other creative minds continue to come up with new applications of digital technologies to existing processes.
The above-mentioned tech state-of-the-art technologies overlap each other, connecting their potential, and so do their benefits.
Industry 4.0, although called a revolution, is more of an evolutionary process. The changes that occur, however dynamic, are spread in time. Implementation of modern technologies involves the assessment of the manufacturing company’s condition, potential, and goals. Only then the right solutions can be applied to shape the industry’s future. Unprecedented advances are ahead, emerging from the mix of powerful automation, innovations, and unrestricted access to remote experts in real-time.
The 4th Industrial Revolution is happening right now, affecting current operations, and preparing companies to face future challenges.
The overall impact on manufacturing is yet to be seen in the upcoming years or even decades, as technology is still growing stronger. What is already certain, is that the changes will continue, bringing new quality in the fields we thought we knew. Companies can achieve significantly better results utilizing state-of-the-art solutions, developing products and processes in ways impossible not that long ago.
The growth of technology affecting the manufacturing industry shows the ongoing shift:
- Predictive maintenance algorithms enable saving over 10% on each avoided breakdown, translating into 2-3% growth in revenues.
- The 2020 IFR report presents 2.7 million industrial robots operating in manufacturing facilities worldwide.
- The IoT market is forecasted to be worth $ 4 trillion this year
Still curious about how today’s manufacturing changes for the better in times of Industry 4.0? Download the free ebook, and indulge in reading our introduction to augmented reality in industrial processes.
Finished the ebook and ready for more? Book the free demo, and see how your manufacturing facility can grow in the 4th Industrial Revolution.


























