Any unexpected interruption in production means huge losses for the company. That is why it is so important to recognize irregularities and faults in advance, which can significantly eliminate costly downtime. This is what preventive maintenance is for, but with the development of artificial intelligence, it is slowly being replaced by innovative predictive maintenance. It is worth knowing what it is and what benefits it can bring to the factory. In this text, I compare preventive maintenance vs predictive maintenance, describe the difference between them, and briefly explain what each method involves.
What Is Preventive Maintenance?
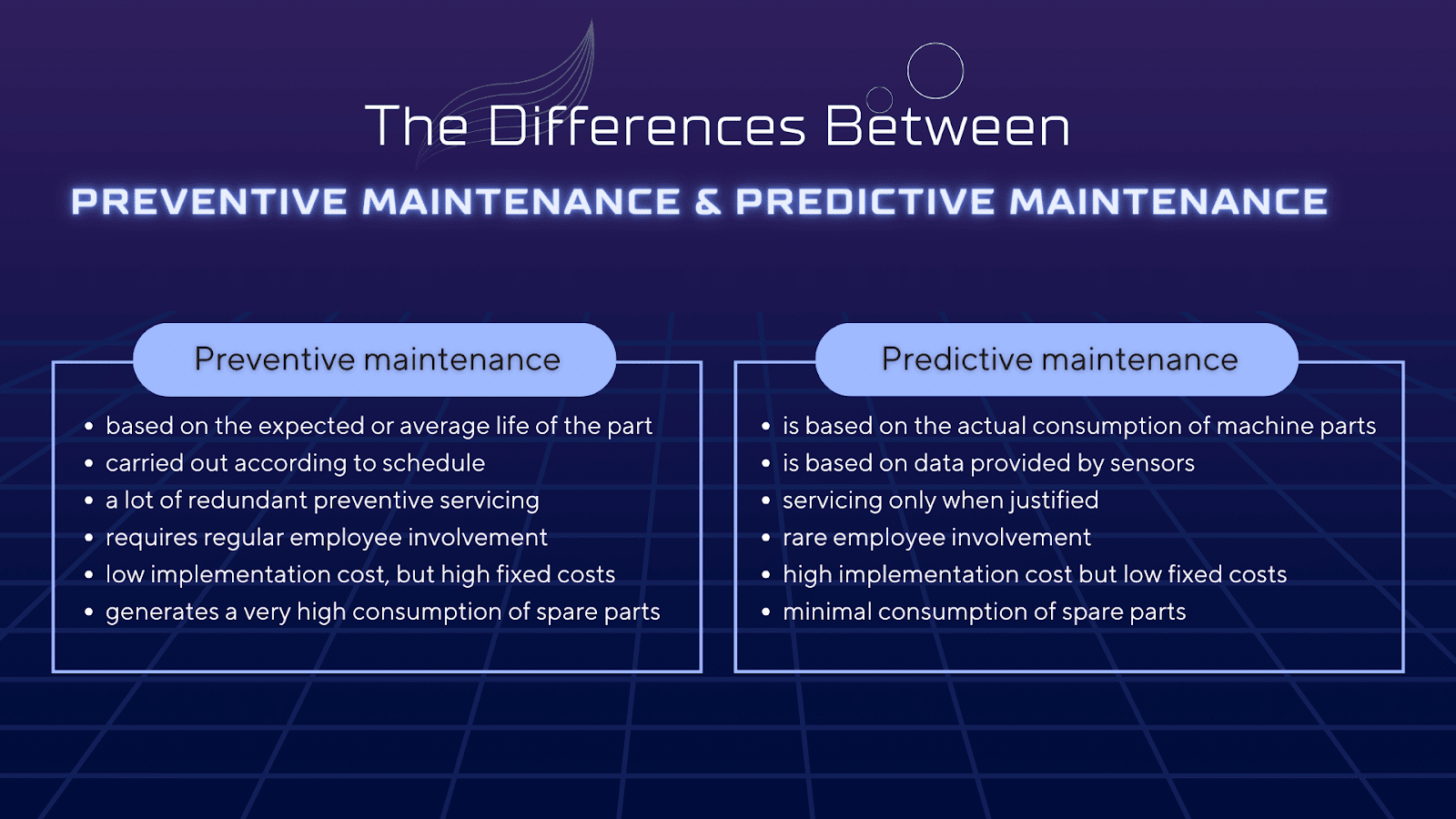
Preventive maintenance (PM) means checking and servicing machines on a scheduled basis. This even includes component replacements on a predetermined schedule. In PM, the technician locates weak points in production lines, such as bearing parts, that are subject to vibration, excessive temperature or any other difficult working conditions. Then, he repairs or maintains them. All this ensures that these weak points do not cause failures in the future.
Generally speaking, preventive maintenance minimizes problems that could negatively impact the maintenance of a production plant. Such issues include significant delays, long-term downtime, or decreased production efficiency. Preventative maintenance planning means constantly reviewing all elements of the production process to eliminate potential failures. Currently, it is the most popular method of maintaining production lines, but predictive maintenance is gradually replacing it, especially in sustainable manufacturing.

What Is Predictive Maintenance?
Predictive maintenance (PdM) is a modern type of production line maintenance based on artificial intelligence and manufacturing automation. It uses complex algorithms and machine learning methods to predict potential equipment failures before they occur.
PdM monitors machine and process parameters to detect and solve problems before they occur. All these thanks to the ability to continuously monitor the operational status of machines and components in real-time.
How exactly does predictive maintenance work in manufacturing? Machine learning specialists collect operational data from machines and use it to develop predictive models. These models then monitor the machine’s condition and verify whether the parameters are within acceptable operating ranges.
For example, a predictive model may require a machine to be technically stopped earlier than planned due to the detection of anomalous values in the sensors of a specific area of the machine.
Preventive Maintenance Vs Predictive Maintenance: The Difference
To compare preventive maintenance vs predictive maintenance, it is necessary to distinguish several key aspects of maintenance. Therefore, below, I explain the difference between preventative maintenance and predictive maintenance by comparing their approach in terms of, among others, planning maintenance work, operating costs, and required technical infrastructure.
Preventive Maintenance Vs Predictive Maintenance: Scheduling Basis
Predictive and preventive maintenance differ primarily in scheduling approaches. PM is conducted on a regular, predetermined schedule, regardless of the actual condition of the equipment. This method involves routine maintenance activities at fixed intervals. In contrast, PdM is scheduled based on the real-time condition of the equipment. It focuses on monitoring and analyzing equipment performance to predict and prevent potential failures before they occur, thus aligning maintenance activities with the specific needs of the equipment.
Preventive Maintenance Vs Predictive Maintenance: Costs
Preventive and predictive maintenance differ significantly in cost implications. PdM, focusing on routine tasks at regular intervals, typically costs less to implement. In contrast, predictive maintenance demands a higher initial investment for establishing monitoring and analysis systems and training and resourcing. However, this upfront investment in predictive maintenance pays off over time. It optimizes maintenance tasks and cuts down labor and material expenses, as it targets maintenance activities based on actual data-driven needs rather than a fixed schedule.
Maintenance Philosophy
In PM, the approach involves maintaining parts in good condition through scheduled routines, not considering each component’s specific state or performance. PdM, however, adapts its activities to the actual condition of the machine. It leverages data analysis to identify and address specific maintenance needs, leading to more efficient and targeted repairs. This distinction highlights how preventive maintenance follows a fixed schedule, while predictive maintenance tailors its interventions to real-time equipment conditions.
Operational Impact
Planned downtime, inherent in preventive maintenance, manages capacity reduction more effectively than the unpredictable and often severe downtime of reactive maintenance. Here, costs and durations remain uncertain until diagnosis and resolution. Conversely, predictive maintenance actively allows repairs during ongoing machine operations, significantly minimizing interruptions. When a shutdown becomes necessary under PdM, it’s brief and precisely targeted, tackling specific issues identified through data analysis. This approach proactively reduces both the frequency and impact of equipment downtime.
Factory Maintenance
In a factory setting, the opposition to preventive maintenance vs. predictive maintenance is clear. PM uses basic tools and equipment for routine tasks based on a set schedule, focusing on regular inspections and servicing without complex tools. On the other hand, predictive maintenance requires a more advanced setup, integrating sensors, data collection, and analytics software for continuous, real-time monitoring. This approach often involves IoT devices and sophisticated data processing, allowing for extensive data analysis and precise maintenance based on the actual condition of the equipment.
What Technologies And Devices Do You Need For Predictive Maintenance?
Above all, adopt modern technologies, especially those included in the digitalization of Industry 4.0, for reliable predictive maintenance in your manufacturing. Moreover:
- Equip machines with sensors and IoT devices to gather real-time data while data acquisition systems store it.
- Use tools like vibration analysis equipment and thermographic devices for machine condition assessment. Employ advanced analytics and AI for predicting failures.
- Manage data efficiently with cloud computing and ensure smooth transmission through communication networks.
- Empower maintenance managers with user-friendly dashboards.
- Leverage augmented reality in manufacturing with industrial-grade AR glasses for remote technician support and enhance repair precision.
- Integrate these systems with your enterprise resource planning (ERP) for optimized maintenance scheduling and operational efficiency.
To see how the AR platform can support maintenance processes in your company, book the free demo, and see how your manufacturing facility can grow with predictive maintenance.

presentation to try
Nsflow in action
Will Preventive Maintenance Completely Replace Preventive Maintenance?
Given that each has unique roles and advantages in maintenance management, depending on factors like equipment type, operational importance, budget, and goals, predictive maintenance is unlikely to replace preventive maintenance completely. Simpler equipment often fares well with the cost-effective, straightforward preventive approach.
However, with significant investments in technology and combat training, “preventive maintenance vs. predictive maintenance” PdM is suitable for operations where equipment failure leads to significant downtime or safety hazards. Many organizations, recognizing these differences, are adopting a hybrid approach. They use PM for routine, less critical tasks and reserve PdM for more essential equipment.
This strategy, integrating both methods, is tailored to an organization’s specific needs and resources. It aligns with Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) principles, a broader approach that will be further discussed.
Briefly About Total Productive Maintenance (TPM)
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) combines preventive and predictive maintenance to enhance machine efficiency and reduce production costs. It’s a comprehensive strategy aiming for company-wide improvements through organized work, focusing on two key elements: planned maintenance and quality maintenance.
- Planned Maintenance – proactively maintains equipment with regular checks and maintenance, aiming to reduce failures and downtime significantly. It includes preventive maintenance following manufacturer guidelines and predictive maintenance for early fault detection, using tools like vibration measurement instruments for prevention.
- Quality Maintenance – entails rigorous analysis of error causes and dedicated efforts to eliminate them. Specialized software allows anomaly detection in machinery and in-depth analysis to pinpoint error sources. Eliminating these root causes prevents future recurrences, enhancing the final product’s quality.
Preventive Maintenance Vs Predictive Maintenance. A Conclusion
Concluding, the active exploration of “What is the difference between preventive maintenance and predictive maintenance” reveals a critical choice in maintenance management. PM provides a cost-effective, straightforward solution for regular tasks, while predictive maintenance leverages advanced technology for critical operations with data-driven precision.
Many organizations actively integrate both, forming a hybrid approach that optimizes efficiency and minimizes downtime. So, it is not about preventive maintenance vs predictive maintenance, but about the balance. This balanced application of both methods embodies a well-rounded and effective strategy within the Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) framework in response to varying equipment and operational needs.


























