In the era of technological gallop, the maritime education and training field is undergoing a significant transformation. At the heart of this evolution is integrating cutting-edge technologies such as augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR). All this is transforming training methods for maritime professionals. But what will be the future of marine training?
Discover AR convergence, enhanced security protocols, and digital learning environments. Check out how they are changing the landscape of maritime education.
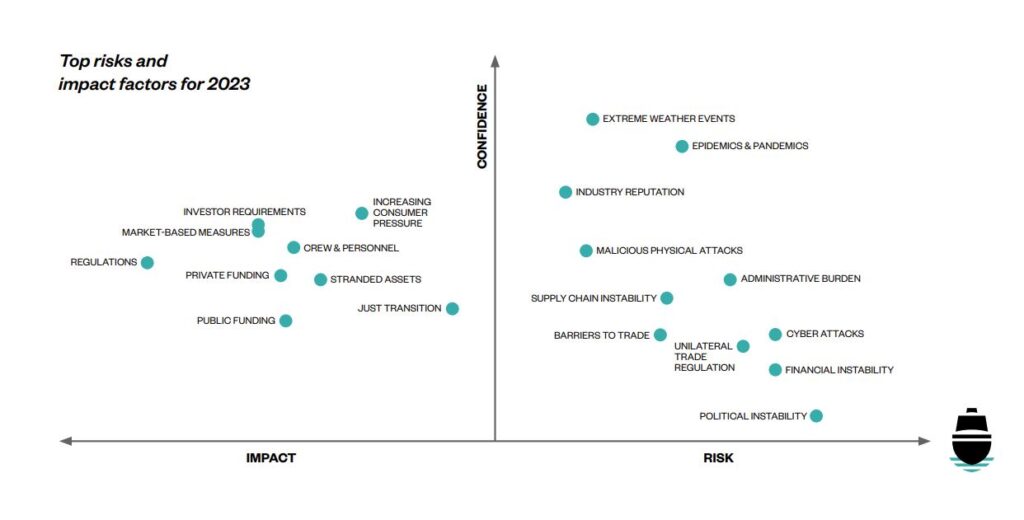
The Industry Challenges
Soon, the maritime sector will use increasingly sophisticated equipment and technologies. The aim is, among other things, to increase the safety of ships and cargo and to improve route planning and navigation. In addition, the industry is looking forward to technological solutions that will enhance transshipment and energy efficiency monitoring and control. Prevention of ship-source pollution and environmental management is also extremely important, as the maritime transport industry is expected to become carbon-neutral by 2050.
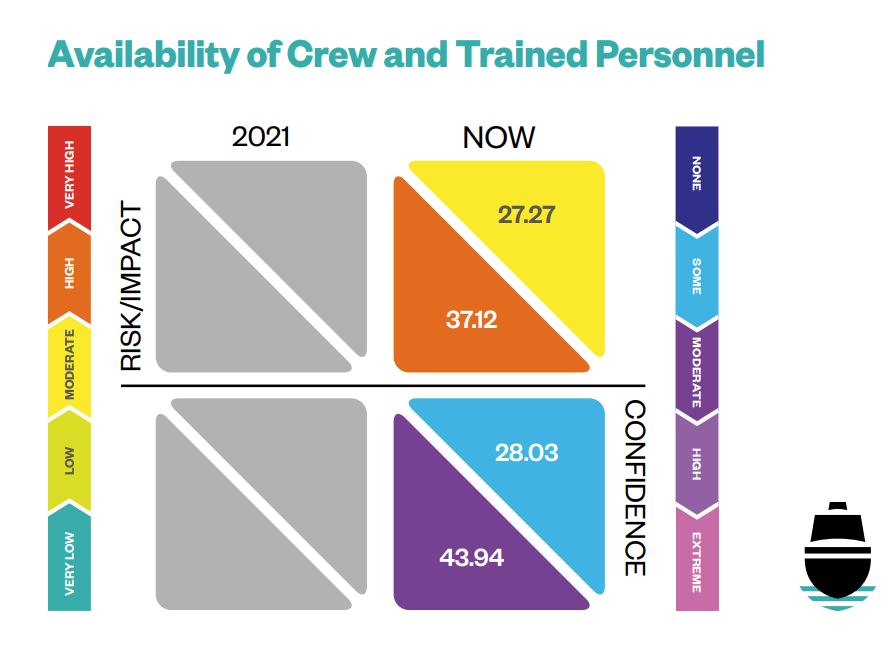
Undoubtedly, the availability of competent and high-caliber crews is a growing issue for ship operators, especially with an expanding global fleet operating in a more fractured geopolitical landscape. The DNV research indicates that as many as 800,000 seafarers will require upskilling by the mid-2030s, adding to maritime operators’ significant crewing pressures. The maritime industry’s operating landscape should secure its foothold, including training, technologies, economic impact, policy formation and more.
The Current Landscape
Physical classrooms and onboard training continue to dominate the maritime training landscape. The courses educate crews on safety, maintenance, and more advanced navigation and technical programs.
However, traditional courses have gaps, particularly in adapting to rapidly changing maritime technologies and global shipping regulations. Maritime training faces two main challenges. Firstly, the need to adjust programs to the changing requirements of the industry. Secondly, adapting methods to new technologies like AR platforms. This mainly includes integrating environmental management and digital navigation training, where many current solutions are lacking.
Technology Integration
Technology integration into maritime training plays a key role in bridging these gaps. Technological advances not only improve existing training methods but also introduce new paradigms in learning.
For instance, advanced computer models used in AR maritime training allow trainees to learn in a secure environment while using actual machinery with computer-generated elements and functions.
Another way to improve training as a whole are e-learning and LMS platforms. They can provide seafarers with more accessible and flexible learning opportunities, enabling continuous learning even at sea. Moreover, they allow centered management of training, the training process, results, and documentation of trained employees.
Technology integration helps equip maritime professionals with the skills necessary to operate in an increasingly digital and automated naval environment. At the same time, it prepares crews for the challenges of modern seafaring.

Hands-On Maritime Training
In their research, DNV highlights insights from industry experts who stress the importance of having simulators and replicas of engines and automation systems in training centers and schools. These tools are crucial for providing hands-on learning experiences and enabling voice and hand gesture control.
The experts also highlight the growing significance of Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) tools, along with simulator-based learning, in developing digital skills. They note the urgent need for parts of the industry to upgrade their training facilities.
This upgrade should include replicas of engine rooms, automation systems, and VR/AR tools. Moreover, experts emphasize the need for more advanced, high-tech training facilities to prepare seafarers for the coming decades’ challenges adequately.
AR In Maritime Training
Augmented reality is rapidly emerging as a game-changer in maritime education. It offers transformative possibilities far beyond traditional training methods, holding immense potential for maritime training. The industry already utilizes AR in maritime transport, streamlining sea shipping operations with process optimizations.
AR provides seafarers with a more engaging and realistic learning experience by superimposing virtual elements onto physical training scenarios. For instance, AR can simulate challenging sea conditions or emergencies, allowing trainees to practice and hone their skills in a safe, controlled environment. Additionally, by conducting remote support sessions, trainers on land can train crews at sea remotely. They have complete control over this process in real-time.
This hands-on approach enhances skill development and significantly improves knowledge retention. As the maritime industry continues to evolve, AR stands poised to revolutionize how maritime professionals are trained, equipping them with the remote training tools and experiences necessary to navigate modern seafaring’s complex and dynamic nature.
Additionally, with augmented technology, maritime employees gain effective practical training in various thematic areas with very limited involvement of instructors. This means better standardization of the knowledge transfer process, independence from the instructor’s specificity, and better measurability of training effects. AR training can also improve the management of changes in training materials.
Innovations in Safety Training Techniques
Recent years have witnessed a surge in innovative safety training techniques within the maritime industry. These emerging tools and methods are set to reshape safety protocols. Modern technologies are revolutionizing safety training, allowing for a more engaging experience.
Additionally, advanced data analytics and machine learning are also playing their parts in developing predictive models for safety management. This helps increase the capability to predict and mitigate potential risks. Technological and AI innovations are not only making maritime safety training more effective. They can also contribute to creating a safer and more informed maritime workforce for the future.

Impact Of Artificial Intelligence In Maritime Training
In the rapidly advancing maritime industry, artificial intelligence is becoming crucial, not only driving competitiveness but also reshaping maritime training. Lloyd’s Register and Thetius report predicts that the AI and autonomous ship market will hit USD 5.01 billion by 2028, highlighting its potential for financial stability and environmental benefits.
AI’s role extends to machine learning algorithms that optimize shipping routes and resource usage and revolutionize maritime professional training. These technologies offer enhanced training methods, improving safety, operational efficiency, and environmental compliance. This article delves into the transformative impact of AI in maritime training, exploring its benefits and challenges in preparing a new generation of maritime professionals for a more sustainable shipping industry.
Incorporating Artificial Intelligence in maritime training brings many benefits, enhancing the training process’s efficiency and effectiveness. Such as:
- customized learning experiences
- simulation and virtual reality
- predictive analytics
- enhanced safety training
- automated assessment and feedback
- real-time decision-making training
- language processing for global training
- long-term skill tracking and development
Integrated learning
Last but not least, it is worth noting that as technological change accelerates in the maritime industry, it is increasingly important to ensure that trainers train crews based on current technologies. This requires constant contact between the training staff and the industry.
As education and skills are the foundation of growth and prosperity, maritime training must prepare people with the competencies, skills, and attitudes that prepare them for industry challenges. Integrated maritime training allows employees to learn from industry experts in the classroom or on the job. This is crucial for the development of their competencies.
Moreover, thanks to integrating university programs with the maritime industry, entities in the marine sector can acquire qualified employees. At the same time, integrated teaching supports maritime education students in developing their potential at the beginning of their professional careers.
A Conclusion
In conclusion, the future of maritime training should provide workforce skills through work-based learning, innovative and flexible training, continuous education and training, etc. It is clear that training methods will be changed by technological advances such as augmented reality and artificial intelligence. These methods have increased worker productivity and are essential in preparing a competent and flexible maritime workforce. Incorporating technological innovations into training programs is crucial to the development of the industry and significantly impacts global shipping, safety, and environmental management.

























